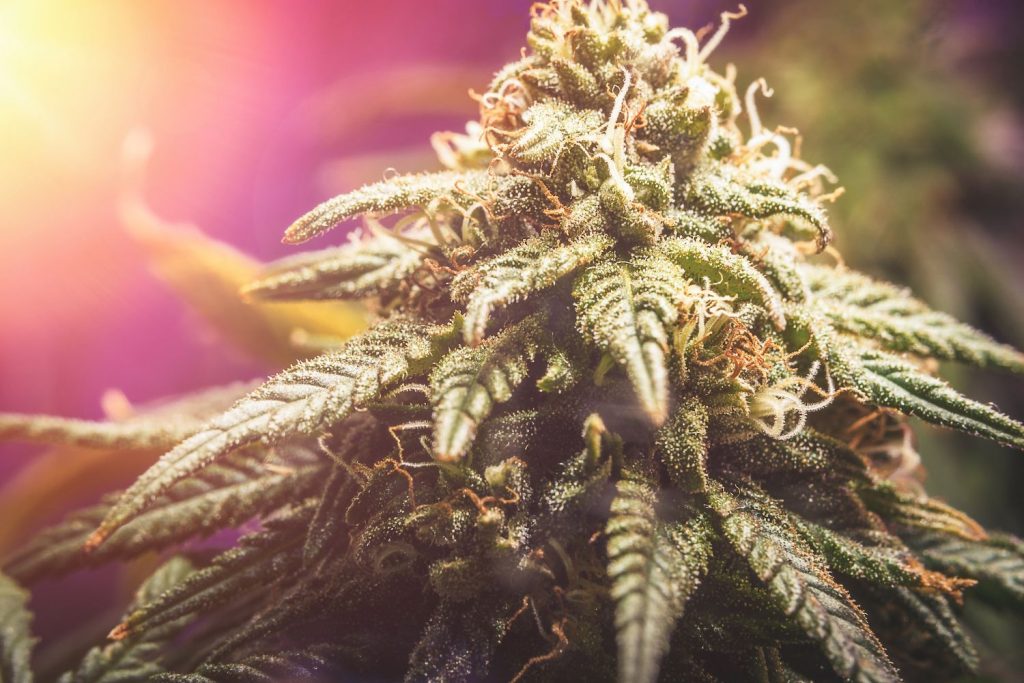
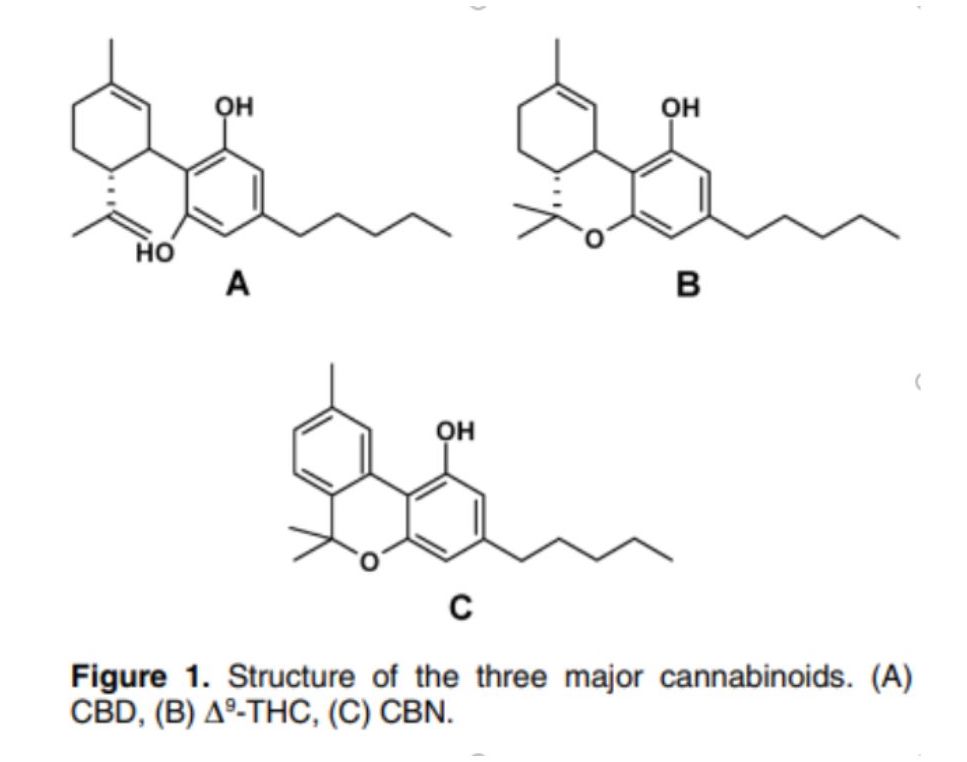
You’ve probably heard all about the two most well-known major cannabinoids, THC and CBD. Meanwhile, the cannabis plant also produces many other minor cannabinoids like CBN (cannabinol). THC appears to break down into CBN over time or with heat, which is why CBN is commonly referred to as “older THC”. For that reason, it’s usually present in high amounts in older cannabis plants.1
CBN has a distinct effect than the other major cannabinoids, THC and CBD. While the research on CBN and sleep remains inconclusive, CBN is believed to be non-intoxicating at therapeutic doses and is gaining more recognition for its ‘sedative effect’ as a sleep aid and for pain management. This means it slows down the body to relax, which may be done by reducing mental distraction, calming active muscles, or generally enhancing physical comfort.
Although THC and CBD have traditionally been the focus of cannabis research, other plant cannabinoids (phytocannabinoids), such as CBN, have unique therapeutic properties that may contribute meaningfully to the “Entourage Effect” of cannabis.3
Pro-Tip:
Sleep disturbances are frequently reported as one of the primary reasons for taking medical cannabis, and there is growing interest in the therapeutic potential of cannabinoids to treat sleep disorders. However, many people are concerned about the potency of THC, so they turn to CBD, a non-sedative that is typically used to treat pain and anxiety during the day. CBN may be used as an alternate therapeutic option as it has been anecdotally reported to help in sleep and with a significant lower risk of intoxication.
CBN is also being studied for potential uses as an anticonvulsant, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory agent.1

Although CBN doesn’t currently have any known side effects, this doesn’t mean that they don’t exist. It just means that CBN hasn’t been studied enough to discover them.
If you are struggling with sleep disorder, chronic pain or emotional distress and considering CBN, we recommend speaking to a Healthcare practitioner for tailored treatment.
If you have any other questions about our products or services, please don’t hesitate to call us at 1-844-756-7333 or email us at info@starseed.com.