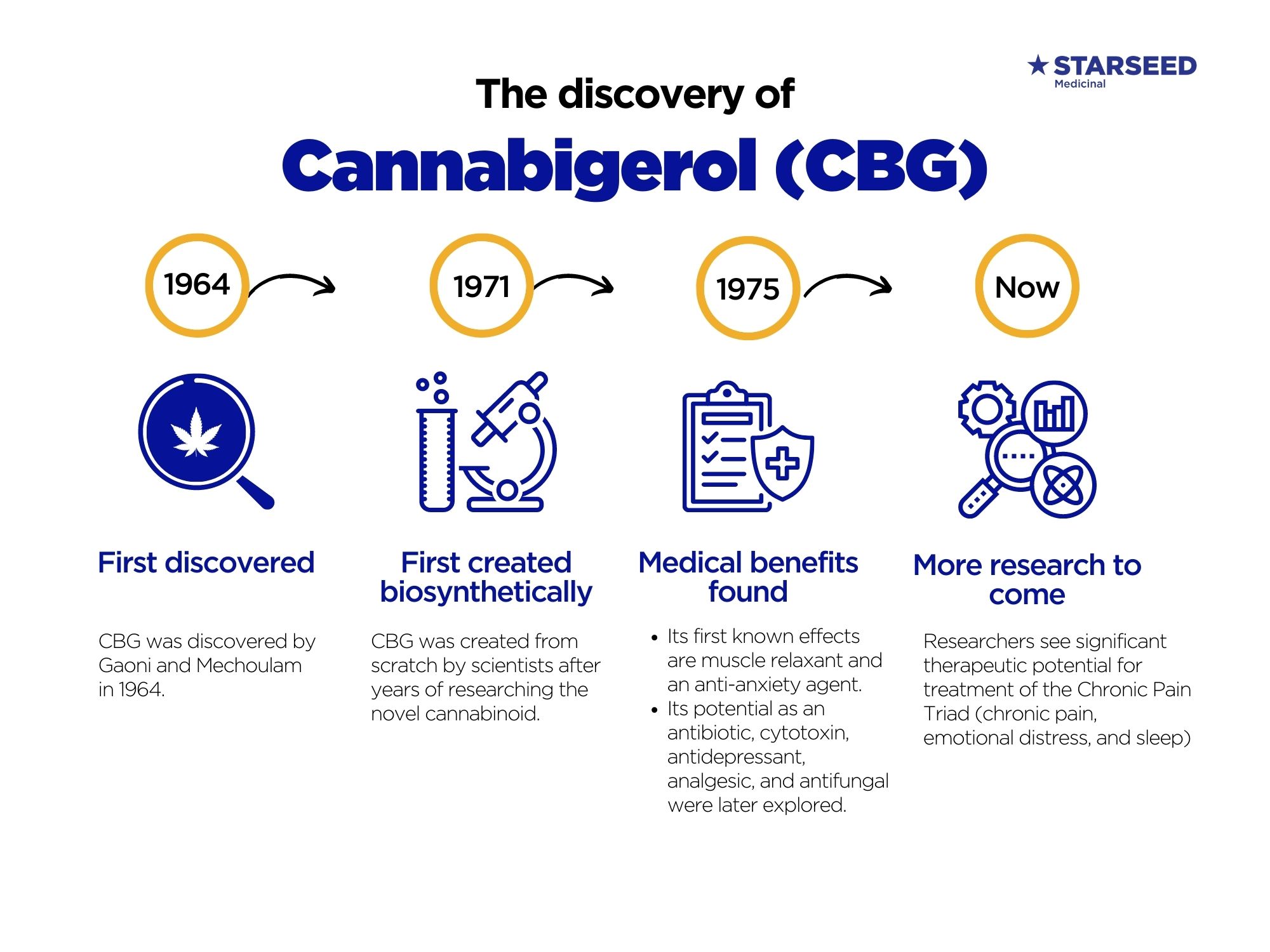
CBG (cannabigerol) is a type of cannabinoid derived from the cannabis plant. CBG, like CBD, is non-intoxicating (it does not get you high) and can be used as an alternative or supplement to CBD and THC-based cannabis products. It is known as the “mother of all cannabinoids” and is a remarkably versatile compound with significant therapeutic promise.
Here are several areas where CBG has shown potential therapeutic effects in preclinical animal studies:
– Neurological illnesses such as Huntington’s disease (HD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Parkinson’s disease (PD) and multiple sclerosis (MS)
– Gastrointestinal diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
– Chemotherapy-induced nausea and cachexia
– Antibacterial agent
Although this research into CBG has shown promise, there is still much to understand and more research on its efficacy and long-term effects is required.
How is CBG used today?
A team of American scientists recently examined the perceived therapeutic effects of consuming CBG-dominant products in humans (see Figure 1 below).
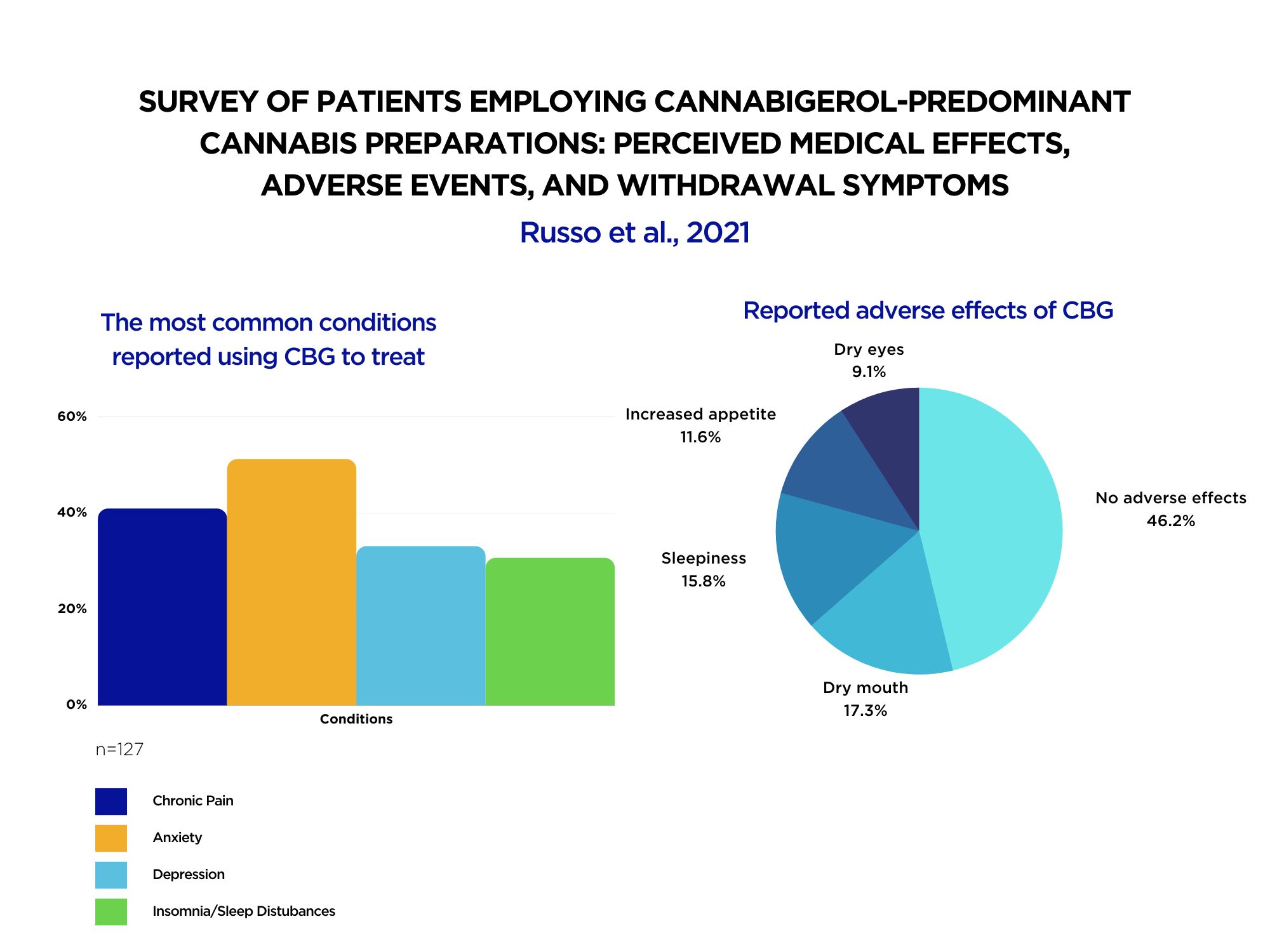
Anxiety (51.2%), chronic pain (40.9%), depression (33.1%), and insomnia (30.7%) were the most frequent medical conditions reported to show efficacy. In addition, a significant proportion of people reported stopping taking the top three drug classes—antidepressants, non-opioid analgesics, and proton pump inhibitors. The most frequent side effects were dry eyes, dry mouth, sleepiness, and increased appetite.
Why is CBG so exciting?
Anxiety appears to be one of the most common indications for CBG, with patients reporting benefit. And anxiety can be difficult to treat because some anti-anxiety medications, such as benzodiazepines, are not widely accepted and might have negative health consequences such as addiction, memory loss, etc.
Can CBG be an alternative for anxiety? It is certainly a desirable alternative.
While preclinical and clinical studies indicate its efficacy in various conditions, further research is necessary to fully understand CBGs therapeutic potential and optimize its use as a medicinal agent.
Please contact our client care team at 1-844-756-7333 or speak to your healthcare practitioner if you have any questions about Starseed’s CBG products.