Good nutrition is essential to maintain your health throughout your life. A healthy diet lowers the likelihood of developing chronic disease. People with chronic diseases can manage their symptoms and prevent complications by eating healthy.
Furthermore, by knowing what types of meals to consume, or avoid, prior to administering cannabis dosages, patients can develop better wellness regimens for their situation. Let’s look at some important nutritional factors to take into account when discussing medical cannabis!
What are Omega-3 fats?
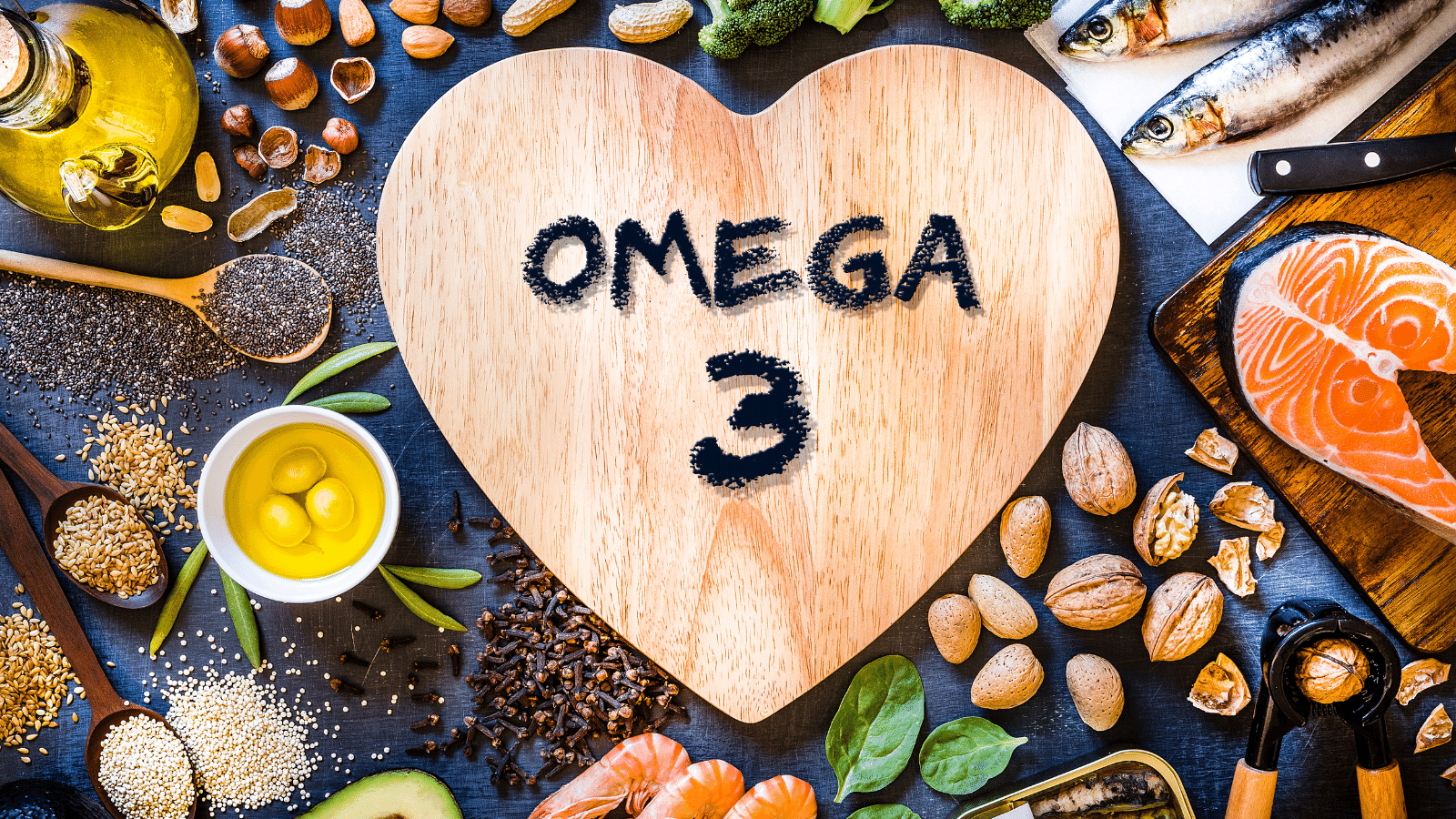
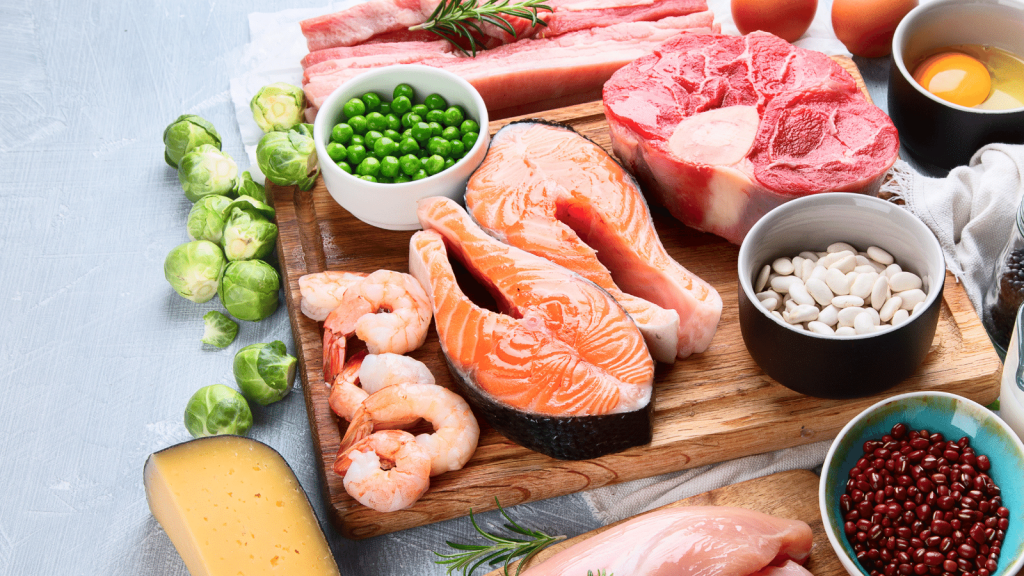
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for overall health in people of all ages. They are well-known for their benefits in preventing heart disease in older adults and their involvement in brain and eye development in babies.
Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids can be found in foods such as meat, eggs, fish, and nuts.
Omega-3 fatty acids act as an anti-inflammatory and support optimal health when consumed in sufficient amounts.
Omega-3s And Your Endocannabinoid System
Most people are unaware of the relationship between omega-3 fatty acids and the endocannabinoid system (ECS), which is thought to be maintained in balance by omega-3 fatty acids.
The ECS is a crucial system of neurotransmitters throughout the entire body that plays an important role in:
– Pain
– Hunger
– Stress response
– Inflammation
– Sleep
– Muscle movement
– Energy
– Mood
Patients may respond more favourably to their cannabis therapy if their diet contains enough omega-3. According to preclinical mice studies, eating enough omega-3 fats results in increased endocannabinoid signalling and stronger sensitivity to the cannabinoids THC and CBD.[1]

Can you combine caffeine with cannabis?
Each day, billions of people rely on caffeine to wake up, or to get through that night shift or an afternoon slump. Chemically speaking, caffeine has been found to increase the secretion of adrenaline and cortisol, which increase wakefulness, increase blood pressure and energy levels. They are the cause of caffeine-induced body stimulation.
It turns out that cannabis functions similarly.
Different cultivars interact with the ECS differently due to their distinct genetic make-up (i.e., cannabinoids, flavonoids, and terpenoids). Some cultivars have a stimulating effect similar to that of caffeine.
However, other patients with a history of anxiety or cardiac issues may react negatively to this combination. On the other hand, some patients who battle with low energy and low mood may find this beneficial.

Medical Cannabis and Gastrointestinal Health
The gastrointestinal (GI) system has cannabinoid receptors, which is why some illnesses, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), often respond effectively to medical cannabis. The GI tract’s cannabinoid receptors seem to control symptoms including pain, inflammation, and nausea, which are all frequent IBS symptoms.
Bacteria in the GI tract (microbiome) may influence endocannabinoid tone. Bacteria quality can influence mood, gut motility, and brain health. It’s interesting to note that some researchers are looking into the relationship between chronic diseases like Parkinson’s disease and the gut-brain axis.
There have been some theories and proposed mechanisms for how cannabinoids, and CBD in particular, may benefit the microbiota. In one study, cannabinoids were used to improve the health of people with alcohol use disorder (AUD)[2]. AUD frequently results in inadequate nutrition as well as liver, intestinal, and brain injury from alcohol. The study discovered that cannabinoids decreased inflammation, regulated gut bacteria, and decreased intestinal permeability in AUD, all of which were beneficial for the microbiome’s general health.

If you have questions about your dietary with medical cannabis regimen, please speak to your healthcare practitioner for a tailored medical cannabis treatment plan to your needs!
Don’t have a medical cannabis document yet? Book an appointment with a healthcare practitioner today!